Washington (AP) – The chemical sprayed on the 2010 BP oil spill may not have helped crucial petroleum-munching microbes get rid of the slick, a new study suggests.
And that leads to more questions about where much of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill went. If the new results are true, up to half the oil can’t be accounted for, said the author of a new study on the spill in the Gulf of Mexico.
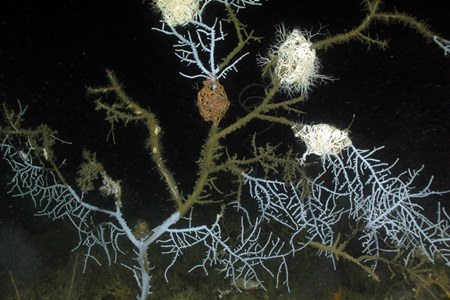 This Sept. 26, 2011 photo provided and taken by Florida State University oceanographer Ian McDonald via an unmanned submersible vehicle, 35 miles from the site of the Deepwater Horizon rig explosion and oil spill, shows Hypnogorgia pendula coral with injuries attributed to the oil spill. The chemical sprayed on the 2010 BP oil spill may not have helped crucial petroleum-munching microbes get rid of the slick, a new study suggests. (Ian MacDonald/Florida State University via AP)
This Sept. 26, 2011 photo provided and taken by Florida State University oceanographer Ian McDonald via an unmanned submersible vehicle, 35 miles from the site of the Deepwater Horizon rig explosion and oil spill, shows Hypnogorgia pendula coral with injuries attributed to the oil spill. The chemical sprayed on the 2010 BP oil spill may not have helped crucial petroleum-munching microbes get rid of the slick, a new study suggests. (Ian MacDonald/Florida State University via AP)
After the 172 million gallon (650 million liter) spill, the chemical dispersant Corexit 9500 was applied by airplane on the slick to help it go away and help natural microbes in the water eat the oil faster. The oil appeared to dissipate, but scientists and government officials didn’t really monitor the microbes and chemicals, said University of Georgia marine scientist Samantha Joye.
So Joye and colleagues recreated the application in a lab, with the dispersant, BP oil and water from the gulf, and found that it didn’t help the microbes at all and even hurt one key oil-munching bug, according to a study published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“The dispersants did a great job in that they got the oil off the surface,” Joye said. “What you see is the dispersants didn’t ramp up biodegradation.”
In fact, she found the oil with no dispersant “degraded a heckuva lot faster than the oil with dispersants,” Joye said.
Joye’s team chronicled nearly 50,000 species of bacteria in the Gulf and what they did to the water with oil, and water with oil and dispersant.
One of the main groups of oil munchers are fat little sausage-shaped bacteria called marinobacters, Joye said. They eat oil all the time and comprise about 3 percent of the bacteria in normal water. But when there’s oil, they eat and multiply like crazy until they are as much as 42 percent of the bacteria, Joye said.
But when the dispersant was applied, they didn’t grow. They stayed around 3 percent, Joye said.
Instead, a different family of bugs called colwellia multiplied more, and they don’t do nearly as good a job at munching the oil, Joye said. She theorized that for some reason the dispersant and marinobacters just don’t work together.
So if the oil wasn’t degraded by the bacteria, the question remains: Where did it go? Joye guesses it might still be on the floor of the gulf.
Outside scientists Jeff Chanton and Ian MacDonald of Florida State University said the study seemed to make sense. Chanton called the results important and surprising.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration welcomed the study and will evaluate to determine how well dispersants work in the future, said agency spokeswoman Keeley Belva.
Online:
Journal: http://www.pnas.org




