Miami (AP) – After a few weeks of working out at CrossFit, Charles Banfield says his back hurt constantly and his joints felt terrible. The 47-year-old’s aches and pains were so bad, he initially blamed his bed and purchased a new mattress.
After feeling a searing pain during a particularly grueling exercise, the Los Angeles-based CEO of an event planning company learned he’d torn his Achilles tendon.
“You miss one step and you could really hurt yourself,” Banfield said.
Though there have not yet been in-depth studies, some chiropractors, doctors and trainers say stories like Banfield’s have become more frequent with the increasing popularity of high-intensity interval training espoused by CrossFit and other similar hybrid workout gyms.
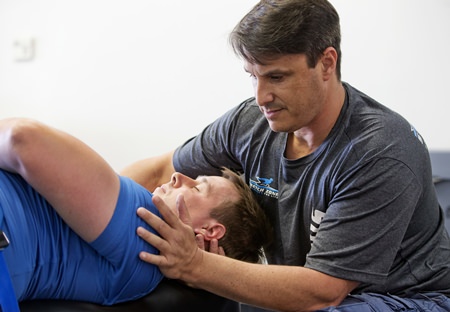 Jorden Gold (right) founder and CSO of Stretch Zone, demonstrates stretching techniques on a client in Boca Raton, Fla. Gold says most popular high intensity workouts are not meant for average gym-goers. (AP Photo/Wilfredo Lee)
Jorden Gold (right) founder and CSO of Stretch Zone, demonstrates stretching techniques on a client in Boca Raton, Fla. Gold says most popular high intensity workouts are not meant for average gym-goers. (AP Photo/Wilfredo Lee)
Such workouts include high-impact moves like jumping onto platforms and are performed during a shorter period of time, often without a break to maximize benefits, but some experts say they strain participants’ bodies beyond what they’re meant to endure as they sling sledgehammers over their shoulders and perfect headstand pushups.
The notion that people are overdoing it has spawned an offshoot industry aimed at delivering lower-impact exercise or to help those recovering from injuries to continue breaking a sweat but without exacerbating their problems.
Many people who do the high-intensity workouts aren’t adequately conditioned for such rigorous workouts, or have back and spine conditions that could worsen, said Marc Umlas, chief of orthopedic surgery at Mount Sinai Medical Center in Miami, who said his office has seen an increase in injuries from workouts at CrossFit and similar programs.
“They plunge headfirst into a high intensity workout and they get injured,” Umlas said.
Torn tendons and ligaments are a common result, he added.
“Every CrossFit athlete that I see as patients, they have something going on as a result of being in CrossFit,” said Dr. Tyler Kallenbach, a Los Angeles-based chiropractor who noted knee and shoulder injuries like torn rotator cuffs are common. He estimated 60 percent of his patients at one point were seeking treatment from CrossFit workouts, where Kallenbach says overtraining is common.
“I’ve got a guy in here who needs his shoulder repaired, a girl who keeps throwing her back out repeatedly. It’s always something with them,” he said.
A spokesman for CrossFit says its likely more doctors are seeing injured CrossFitters but only because so many people are doing CrossFit — not because it’s a more dangerous workout. The brand has over 13,000 locations worldwide. A training program that’s completely safe would be ineffective, company spokesman Russell Berger said.
CrossFit is known for varied workouts that include gymnastics-style moves like handstands and pull-ups, weightlifting, burpees, running and jumping onto platforms, performed at relatively high intensity.
“CrossFit is relatively safe and is as safe as anything else you could be doing,” Berger said.
Although strength training while injured may seem counterintuitive, experts say it’s the best way to heal.
“Stretching can be complementary to a rehab program, but the focus is usually on the strengthening. Often what we’re trying to do is create a balance between strength and flexibility,” said Dr. Kelly McInnis, a sports medicine physiatrist at Massachusetts General Hospital who is a consultant for the New England Patriots and the Boston Red Sox.
Most CrossFit and similar high intensity workouts are not meant for average gym-goers, said Jorden Gold, who founded Stretch Zone, which has 33 locations in Florida and three other states. During the 30-minute sessions, therapists use bolsters and belts to stretch clients on a table from angles that are nearly impossible to stretch on one’s own. Unlike massage, clients are clothed and are stretched in a room with several others.
“The majority have no business being there in the first place. … It’s Olympic training,” said Gold. “It’s probably only suitable for a very, very small percentage that go.”
Los Angeles-based trainer Lauren Roxburgh has created an entire workout around the foam roller, a narrow tube often relegated to post-workout stretching, which she says can smooth out connective tissue, stimulate the lymphatic system and deliver highly effective core strengthening. Roxburgh noticed many clients struggling with injuries from high-intensity workouts and an obsession with training harder and longer.
“In our lifestyle it’s been very much about the doing. … It’s all about pushing through, doing, doing, doing, and it hasn’t been enough about the yin, which is the being, being in the moment, being present in our bodies,” she said.
At LIT Method, a Los Angeles studio that specializes in low-impact workouts for those who are injured, clients rotate between cardio sessions on rowing machines and strength training using resistance bands. Sessions always end with foam rolling and participants’ injuries are written on the side of their rower.
“Eighty-five to 90 percent of our clients are coming in with some sort of injury and they don’t want to get hurt anymore,” said LIT Method co-founder Justin Norris.
He said classes sell out a week in advance: “There was a huge, huge need for this.”




